How AI invites new industry use cases
The age of artificial intelligence is not on the horizon.
It’s here. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) continues to spread with a speed that’s staggering, as it grows even more every day. Companies worldwide have adopted and implemented AI, in solutions that are reshaping industries through improved efficiency, productivity and decision making.
However, the meteoric rise of AI can overshadow some valid concerns around security and privacy.
Many organizations have integrated AI into their business processes more quickly than they have updated security strategies and protocols. This has created complex fractures in outdated programs that leave vulnerable gaps of risk exposure. Your risk, technology and cybersecurity leaders must find, understand and mitigate these exposures.
AI-driven solutions can provide powerful capabilities — for you, and for malicious actors who gain access, data and control from your solutions. Now, many cybersecurity professionals are trying to catch up to rapid AI adoption. But they must go further, to implement forward-thinking strategies that anticipate potential risks, mitigate them and proactively define the security narrative.
Industry use cases for AI
The recent surge in the use and adoption of generative AI (GenAI) technology like ChatGPT has been extraordinary. GenAI has gained visibility due to its free availability, surprising superiority to traditional chatbots, and its rapid integration with search engines like Bing and Google. This powerful AI technology can accomplish a variety of tasks to make our lives more efficient and connected.
In recent months, one case has experienced a meteoric rise in popularity: Content creation. Journalists, bloggers, students and office employees now use GenAI to brainstorm ideas, draft initial versions of articles or papers and polish up their writing. In the education sector, teachers and tutors use GenAI to curate study materials, generate practice questions and simplify complex topics. In many industries, AI-driven language processing can:
- Automate tedious or repetitive work like basic Q&A support and help desk ticket generation
- Enable real-time responses around the clock, without incurring additional human resource cost
- Convert conversation (or “unstructured text”) into insights for more informed decision making
- Break down language barriers to facilitate worldwide support and collaboration
- Help write or debug code, as well as optimize and document existing code — this has some people predicting the end of software development as we know it
In recent years, machine learning and deep learning AI have permeated diverse industries to address complex challenges and enable innovative solutions. These solutions have the potential to transform and disrupt how we work, create and consume. The following use cases illustrate some of the ways AI is applied in various industries and domains.
Healthcare
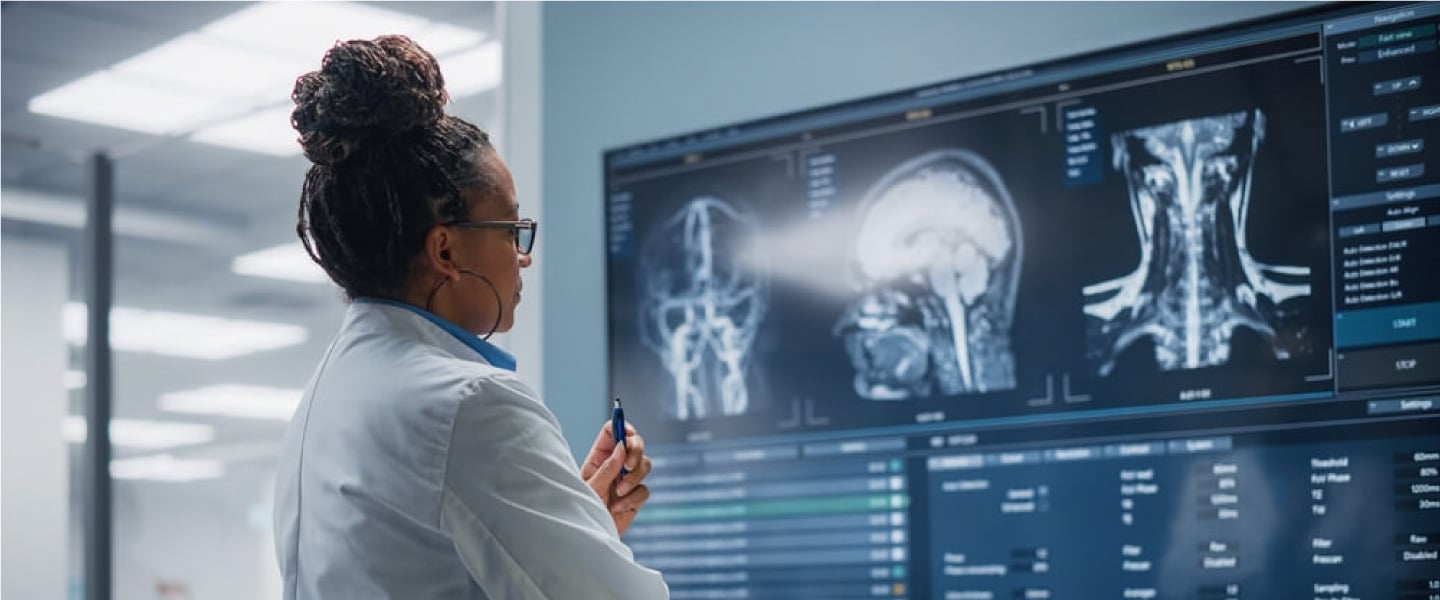
AI systems can analyze ultrasounds, X-rays, MRIs and other medical images to provide insights and inform diagnosis and treatment. For example, the FDA has approved an AI system that can analyze scans to identify signs of stroke and help physicians quickly make treatment decisions. In the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, AI played a significant role in helping to determine responses and treatments. One system uses deep learning algorithms to analyze medical images for features that are indicative of COVID-19. AI has also been used to predict potential mutations of the SARS-CoV-2 virus which causes COVID-19.
Law enforcement
Facial recognition technology can be used to identify individuals by analyzing their facial features and matching them against a database of known faces. This can have many applications such as identifying suspects in criminal investigations or verifying individuals at border crossings or airports, but it also comes with an explicit risk of misuse by governments or companies that might target or discriminate against certain individuals.
Media and entertainment
Image generation technology is not new, but AI has accelerated and drastically improved the quality and speed of creating and augmenting images from various sources. In the past year, revolutionary GenAI image generation tools have emerged that can turn words and pictures into stunning art. Recent advancements also enable users to send audio data through a GenAI model that creates music, sounds or voices.
Automotive and geolocation
Geo-tagging and real-time mapping, which involve the identification, live tracking, and analysis of objects or locations in the real world, are a rapidly growing set of AI use cases. This capability has significant applications in fields like urban planning, disaster management, environmental monitoring and autonomous vehicles. By accurately identifying and interpreting the physical environment, AI-based systems can provide insights and actionable information for decision-makers, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient operations.
Business intelligence and analytics
AI technologies often improve efficiency with intelligent automation, and decision-making processes with reasoned and insightful analysis. In the financial sector, companies have already explored using machine learning for automated investing, portfolio diversification and retirement planning, optimizing returns based on market trends and investor preferences. Credit bureaus now employ AI to analyze non-traditional data points for more precise creditworthiness predictions. AI’s ability to identify anomalies and trends from large data volumes is driving robust fraud detection in banking and retail.
Human resources
The integration of GenAI in HR has transformed talent management and workforce planning. AI tools facilitate more accuracy in automated résumé screening and candidate ranking, reducing the time spent on manual reviews and improving the likelihood of identifying optimal candidates. However, there are legitimate concerns surrounding the widespread use of AI. The primary concern is that potential bias in AI algorithms may drive discriminatory hiring practices or unfair evaluations. There is also a fear of overreliance on technology, which may result in the devaluation of human intuition and judgement in the hiring and HR management process.
Cybersecurity
In the realm of cybersecurity, AI has emerged as a game-changer with numerous applications that are designed to safeguard our digital world.
- Code generation and review: AI code generation can help developers create code more efficiently and accurately, while constantly reviewing the code for vulnerabilities, inefficiencies or faulty logic. This enhances the overall quality and security of software while reducing the time spent on remediating insecure code farther down the software development lifecycle.
- Network intrusion detection systems: These systems can use AI machine learning and reasoning to identify and establish a baseline for a network’s behavior, raising alerts for anomalies or threats. They can even counteract the threats automatically, significantly reducing adversary dwell time.
- Phishing and spam detection: This helps protect users and organizations from unwanted and malicious messages. AI natural language processing and machine learning can identify and block harmful emails. Even large email providers, like Gmail, use AI to analyze email content and sender data, filter out spam, detect sophisticated phishing attempts, and continuously refine their detection algorithms. Browsers and security solutions can also identify phishing websites, analyzing URLs and web content to alert users or block the sites.
- Malware analysis: AI is widely used in malware analysis to monitor system behavior and detect anomalous activity that could indicate a malware infection. AI technologies can also help generate and test malware samples in safe environments, to proactively identify vulnerabilities and develop countermeasures. AI can also help automate and improve the speed and accuracy of incident response to malware attacks. Advanced solutions can automatically quarantine infected systems, identify and block or filter the source of attacks, and provide real-time updates and mitigation strategies to security teams.
AI technologies can enhance cybersecurity tools, and help you detect and respond to threats more effectively, but the same technologies can also be used by attackers.
Related insights
View more


